Dillon, Lucy (2025) A whole-system approach to drug prevention. Drugnet Ireland, Issue 92, Autumn 2025, pp. 11-14.
| Preview | Title | Contact |
|---|---|---|
|
PDF (Drugnet Ireland 92)
3MB |
In May 2025, the Advisory Council on the Misuse of Drugs (ACMD) in the United Kingdom (UK) published a report titled A Whole-System Response to Drug Prevention in the UK.1 It is a comprehensive report that reflects on the evidence for the various components of an effective drug prevention system, including for prevention interventions.
While the report’s focus is on the UK, it should be of interest to prevention stakeholders in Ireland. This article is based on both the published report and a presentation made by the Chair of the ACMD, Professor Owen Bowden-Jones, at a seminar held by the the UK-based Drug Education Forum on 19 June 2025.1, 2
Research aim
The ACMD was commissioned by the UK Government to provide advice on drug prevention for young people aged 11–24 years. The report describes the key foundational principles for long-term drug prevention action for young people, and makes recommendations on:
- ‘a whole-system response to prevention of drug use and related harms, including actions for younger age groups, which have positive effects later in life
- effective labelled (universal, selective and indicated) interventions on prevention, and
- the necessary structural components of a robust drug prevention system’ (p. 3).1
Methodology
The report is based on a review of national and international literature; evidence gathered from UK services delivering drug prevention activities; and the expertise of a specially formed working group comprising national and international experts in the field.
Benefits of prevention
The report is grounded in an understanding of the benefits of drug prevention and it makes the case for its prioritisation as a response to drug-related harms. It describes the cost-effective nature of prevention when considering the high cost of drug-related harms to society, that drug prevention activities can have wider societal benefits, and that it supports other government policy priorities.
Current UK drug prevention system
Early on in the report, the authors conclude that a drug prevention system does not currently exist in the UK. Among the issues facing drug prevention in the UK is that there is no coordinated UK-wide strategy, existing drug prevention is poorly funded, there is no clear prioritisation of interventions, there is a lack of a trained workforce, and there are no systems in place to monitor activities or outcomes.
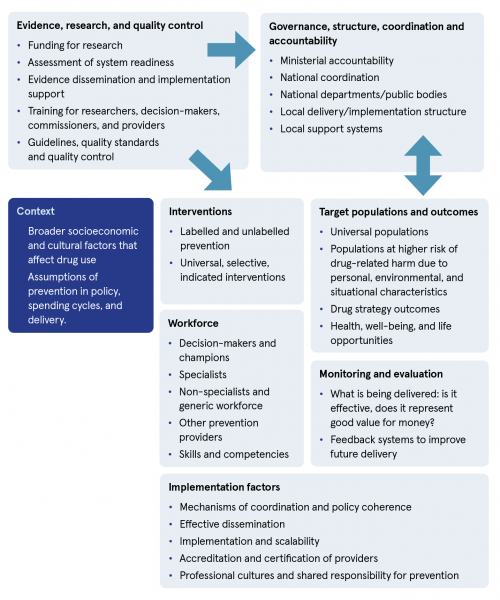
Figure 1: Structural summary of the prevention system map
Source: Advisory Council on the Misuse of Drugs (2025) (p. 12)1
A systems approach
Based on an examination of the evidence, the authors present an idealised prevention map system (see Figure 1). For each component of the prevention system, they describe the current UK position and present the evidence for what a robust version of each would look like.
Recommendations
Two groups of recommendations are made in the report. The first comprises recommendations that relate to the development, implementation, and evaluation of a whole-system drug prevention approach. The second includes recommendations that relate to specific drug prevention interventions.
What is recommended to develop, implement, and evaluate a whole-system drug prevention approach?
Six recommendations are made to the UK Government to support the establishment of a whole-system drug prevention approach:
- Undertake a stocktake of the prevention landscape in the UK and how it aligns with international standards, using a tool such as the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime’s (UNODC’s) Review of Prevention Systems (RePS) tool.
- Monitor quality by developing a national prevention quality standard, and use a dashboard to monitor delivery locally.
- Provide ring-fenced, long-term funding at a local level for drug prevention.
- Support strong local leadership for prevention activities.
- Support national leadership, ideally through the appointment of a national prevention champion.
- Develop a competence framework for evidence-based prevention activities (for labelled and unlabelled prevention work).
Which interventions did the authors recommend based on their research?
The report outlines a wide range of interventions and describes features that appear to contribute to their effectiveness. While they name numerous programmes throughout the report that they consider to be evidence based, in their recommendations, the authors summarise the approaches in which they think the UK Government should invest:
Universal approaches:
- whole-community approaches
- whole-school approaches (including links to mental health support teams)
- parent/carer-based prevention approaches
Selective interventions:
- interventions targeting multiple health risk behaviours and comorbidities, in particular common mental health disorders
Indicated interventions:
- family-based interventions targeting children and young people’s drug use
- family-based interventions to support children and young people affected by others’ drug use (e.g. parental drug use).
In addition to interventions, it is also recommended that the UK Government increase funding to support a long-term approach to evaluation, innovation, and research in order to inform the UK’s evidence base.
Concluding comment
This is a comprehensive report that outlines key features of effective prevention and the limitations of the current evidence base in the field. While the report focuses on the UK context, there are many parallels with the Irish context and the recommendations should be of value when considering the status of Ireland’s prevention landscape. The UNODC’s RePS tool is currently being implemented in Ireland with the aim of informing the next national drugs strategy. This represents an important step in understanding and improving drug prevention in Ireland.
1 Advisory Council on the Misuse of Drugs (2025) A Whole-System Response to Drug Prevention in the UK. London: Advisory Council on the Misuse of Drugs. Available from: https://www.drugsandalcohol.ie/43292/
2 Recording of the presentation is available at: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cRQmPmzWISs
J Health care, prevention, harm reduction and treatment > Prevention outcome
J Health care, prevention, harm reduction and treatment > Substance use prevention > Universal prevention
J Health care, prevention, harm reduction and treatment > Substance use prevention > Targeted prevention
J Health care, prevention, harm reduction and treatment > Prevention programme or service
J Health care, prevention, harm reduction and treatment > Prevention approach
MP-MR Policy, planning, economics, work and social services > Policy > Policy on substance use > Demand reduction / prevention policy
VA Geographic area > Europe > Ireland
VA Geographic area > Europe > United Kingdom
Repository Staff Only: item control page