Millar, Sean  ORCID: https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4453-8446
(2023)
Drug use among 20-year-olds in Ireland: results from the Growing Up in Ireland study.
Drugnet Ireland,
Issue 84, Winter 2023,
pp. 28-29.
ORCID: https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4453-8446
(2023)
Drug use among 20-year-olds in Ireland: results from the Growing Up in Ireland study.
Drugnet Ireland,
Issue 84, Winter 2023,
pp. 28-29.
| Preview | Title | Contact |
|---|---|---|
|
PDF (Drugnet 84)
1MB |
Since 2006, the Growing Up in Ireland (GUI) study, a national longitudinal study of children and young people, has followed a cohort of children born in 1998. Four waves of interviews have been conducted with this cohort, when they were aged 9, 13, 17–18, and 20 years old. The most recent report presents the findings of 5,190 interviews of the 20-year-olds, which were conducted in 2018 and 2019.1 Key findings regarding drug use are discussed below.
Any drug use
Figure 1 shows the prevalence of illicit drug use among 20-year-olds in the GUI study. Cannabis was the most prevalent drug, with 59% stating that they had ever tried it. More than one-quarter (28%) of all 20-year-olds said they had ever tried other non-prescribed drugs, with the most commonly reported drugs being cocaine (22% of all 20-year-olds had tried it at least once), ecstasy (17%), and ketamine (12%).
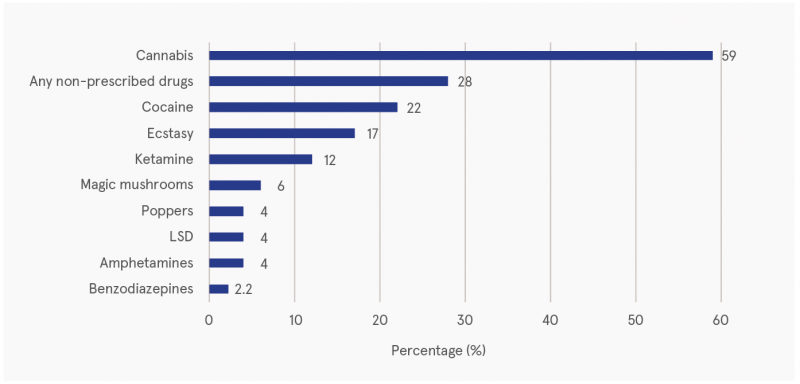
Source: GUI Ireland, 2021
Figure 1: Illicit drug use (at least once) among 20-year-olds in Ireland, 2018–2019
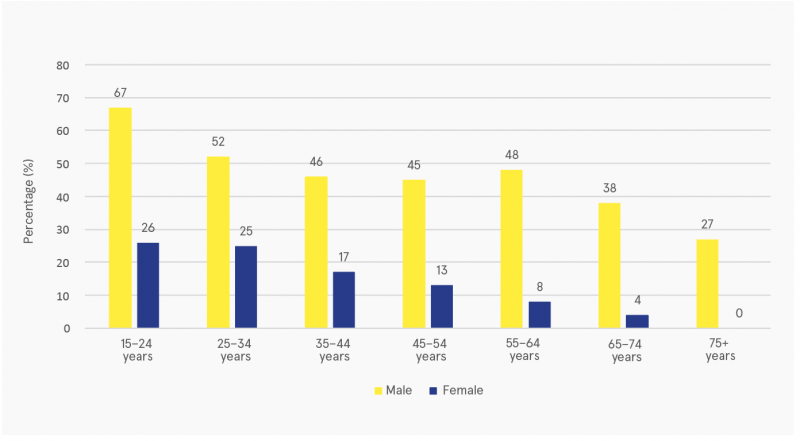
Source: GUI Ireland, 2021
Figure 2: Percentage of 20-year-olds who took cannabis occasionally or more than once per week, according to key background characteristics, 2018–2019
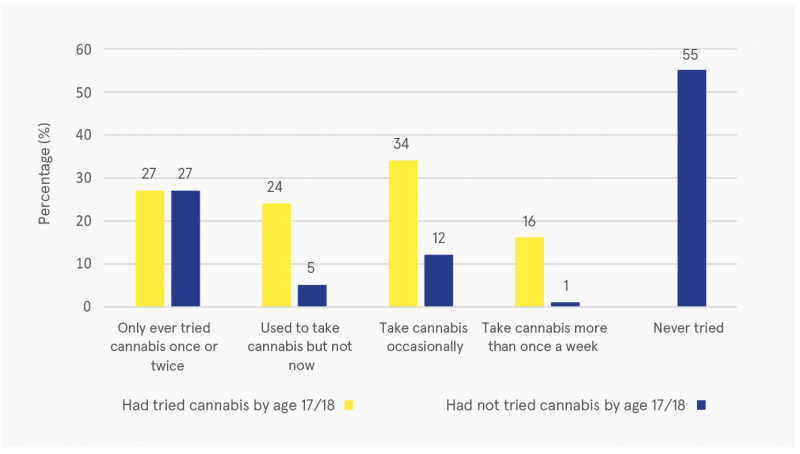
Source: GUI Ireland, 2021
Figure 3: Status regarding cannabis use at age 20, based on cannabis use at age 17/18, 2018–2019
Cannabis use
It was found that almost one-quarter of 20-year-olds used cannabis at least occasionally (Figure 2), with 6% stating that they used cannabis once per week. Differences in the percentage of young adults taking cannabis occasionally or more often were observed in terms of both sex and parental education: a greater proportion of males took cannabis regularly (29% vs 18% females), as did a greater proportion of 20-year-olds whose parents had higher levels of education (degree or more, 28%, vs lower second level or less, 19%).
Prior experience with drugs was also found to be related to current cannabis use (see Figure 3). Young adults who had already tried cannabis by age 17/18 were more likely to be current cannabis users at age 20. In addition, they were more than twice as likely to be occasional users (34% vs 12%) and were also more likely to use more than once a week (16% vs 1%).
1 O’Mahony D, McNamara E, McClintock R, Murray A, Smyth E and Watson D (2021) Growing Up in Ireland: The lives of 20-year-olds: making the transition to adulthood. Cohort ‘98. Report 9. Dublin: ESRI; Trinity College Dublin; Department of Children, Equality, Disability, Integration and Youth. https://www.drugsandalcohol.ie/35334/
Repository Staff Only: item control page