Millar, Sean (2018) Frequently used drug types and intentional drug overdoses in Ireland. Drugnet Ireland, Issue 66, Summer 2018, pp. 18-19.
| Preview | Title | Contact |
|---|---|---|
|
PDF (Drugnet 66)
1MB |
Intentional drug overdose (IDO) is the most common form of hospital-treated self-harm, involved in 65–85% of presentations in Ireland, as reported by National Self-Harm Registry Ireland.1 However, no national study has systematically classified the range of drugs involved using a validated system in Ireland. The Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) system is a World Health Organization-recommended classification system designed to measure drug utilisation at an internationally comparable level.2 Recently conducted research aimed to examine drugs taken in IDO according to the ATC classification.3
In this study, published in the European Journal of Public Health, presentations of IDO in the Republic of Ireland for the period 1 January 2012 to 31 December 2014 were examined and information on demographic and overdose characteristics obtained. Drugs were classified according to their use at the time of ATC system application (December 2016). Illegal drugs were identified using the Misuse of Drugs Acts.4
Results
During the study period, there were 18,329 self-harm presentations involving IDO, representing 67.6% of all self-harm presentations. The majority (58.7%) of presentations were made by females. The majority of IDO presentations involved overdose only (89.5%), with self-cutting identified as the most common combined method, involved in 6.5% of IDOs. Alcohol was present in 40.6% of IDOs and was more common in male presentations (44.7% vs 37.8%, p<0.01). The median number of total tablets taken per IDO case was 23 for males and 20 for females, with over one-third of presentations involving the ingestion of between 20 and 49 tablets.
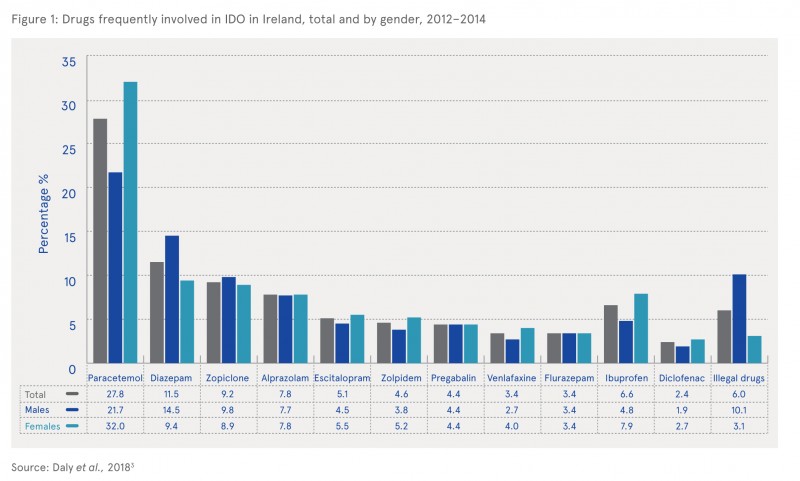
The drugs that were most frequently used in IDO are shown in Figure 1. The most frequently used drug was paracetamol, which was involved in 27.8% of IDOs. Anti-inflammatory drugs (ibuprofen and diclofenac) and antidepressant drugs (escitalopram and venlafaxine) were also frequently taken in IDO (6.6%, 2.4%, 5.1% and 3.4%, respectively). Illegal drugs were involved in 6.0% of IDOs.
Other key findings from the study included the following:
- Significant gender differences were found in relation to drugs involved in IDO. Musculoskeletal system drugs were significantly more common in female IDOs compared with male IDOs (14.0% vs 9.2%, p<0.01). Similarly, IDOs involving analgesics and antidepressants were significantly more common in female presentations (36.4% vs 26.7%, p<0.01 and 23.9% vs 19.1%, p<0.01). In particular, paracetamol was involved significantly more often in female IDOs (32.0% vs 21.7%, p<0.01).
- Illegal drugs were three times more common in male compared with female presentations (10.1% vs 3.1%, p<0.01).
- Alcohol involvement in IDO was significantly higher in male compared with female presentations (44.7% vs 37.8%, p<0.01).
- Alcohol was most frequently consumed in presentations involving illegal drugs (47.8%) followed by anxiolytics (49.3%, p<0.01).
Conclusions
The results from this research suggest that people who engage in IDO frequently take prescription only or sales-restricted drugs, and that IDOs often involve alcohol and/or polydrug use. The authors concluded that the findings highlight the importance of addressing drug and alcohol misuse, potential inappropriate prescribing, and the enforcement of legislation restricting specific drug sales.
1 Perry IJ, Corcoran P, Fitzgerald AP, Keeley HS, Reulbach U and Arensman E (2012) The incidence and repetition of hospital-treated deliberate self harm: findings from the world’s first national registry. PLOS One, 7(2): e31663. https://www.drugsandalcohol.ie/17030/
2 World Health Organization (2018) Guidelines for ATC classification and DDD assignment. Oslo: WHO Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology. Available online at: https://www.whocc.no/filearchive/publications/guidelines.pdf
3 Daly C, Griffin E, Ashcroft DM, Webb RT, Perry IJ and Arensman E (2018) Frequently used drug types and alcohol involvement in intentional drug overdoses in Ireland: a national registry study. Eur J Public Health 28(4): 681–86. https://www.drugsandalcohol.ie/28709/
4 Misuse of Drugs Act 1984. Irish Statute Book. Available online at: http://www.irishstatutebook.ie/eli/1984/act/18/enacted/en/print.html
F Concepts in psychology > Behaviour > Self-destructive behaviour / self-harm > Suicidal behaviour / suicide
G Health and disease > Substance use disorder (addiction) > Drug use disorder > Drug intoxication > Poisoning (overdose)
VA Geographic area > Europe > Ireland
Repository Staff Only: item control page