Millar, Seán  ORCID: https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4453-8446
(2024)
HIV incidence among people who inject drugs in Ireland, 2000–2018.
Drugnet Ireland,
Issue 87, Winter 2024,
pp. 17-18.
ORCID: https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4453-8446
(2024)
HIV incidence among people who inject drugs in Ireland, 2000–2018.
Drugnet Ireland,
Issue 87, Winter 2024,
pp. 17-18.
| Preview | Title | Contact |
|---|---|---|
|
PDF (Drugnet Ireland 87)
2MB |
Globally, there are an estimated 15.6 million people who inject drugs (PWID).1 Among PWID, the risk of acquiring HIV is more than 30 times higher than the rest of the population.2 However, HIV incidence has declined among PWID in Western Europe over the last two decades. In light of this improved situation, a 2023 study investigated changes in HIV incidence in Ireland among PWID from 2000 to 2018.2
In this study, published in the journal Addiction, data on new diagnoses of HIV among PWID, as reported by the Health Protection Surveillance Centre, were examined. New HIV cases in two time periods (2000–2009 and 2010–2018) were compared by sex, age group, area of residence, and country of birth.
HIV incidence
A total of 753 cases were reported in PWID in Ireland between 2000 and 2018. During this time period, HIV incidence among 15–29-year-old PWID in Ireland declined from 5.69 to 0.11 cases per 100,000 persons, equivalent to 0.22 cases per 100,000 annually. Among PWID aged 30–64 years, HIV incidence declined annually by 0.06 cases per 100,000.
Table 1: Comparison of new diagnoses of HIV in Ireland between 2000–2009 and 2010–2018
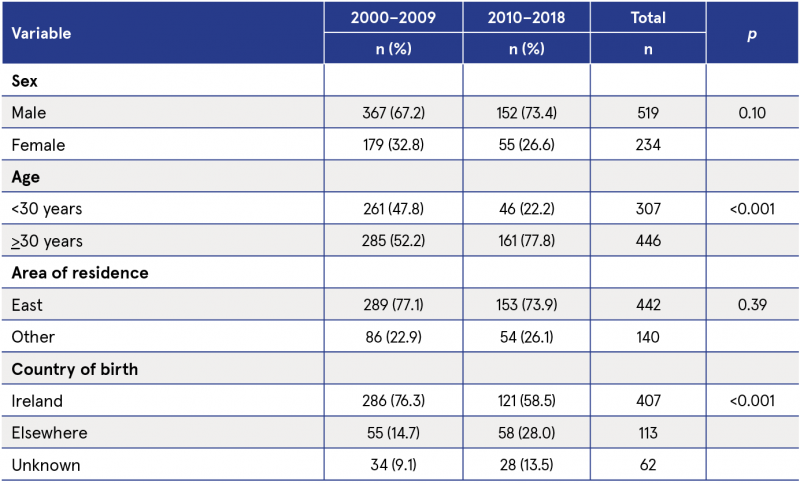
Comparisons of new diagnoses
Table 1 shows the comparisons of new diagnoses of HIV among PWID during the first half of the study period (2000–2009) and the second half (2010–2018). Although there was a small increase in the number of males diagnosed with HIV, this finding was not statistically significant. There was a relative increase in HIV cases among older adults, while those born outside of Ireland accounted for a growing minority of cases (14.7% to 28.0%).
Conclusions
The authors observed that since 2000, Ireland has achieved an ongoing reduction in HIV among PWID and that this reduction has occurred in the context of a reasonably comprehensive health-led and harm-reduction-orientated drugs strategy. Nevertheless, HIV outbreaks among PWID that were observed in 2014/2015 in Ireland highlight the ongoing challenges faced by surveillance, treatment, and harm-reduction services.
1 Degenhardt L, Peacock A, Colledge S, et al. (2017) Global prevalence of injecting drug use and sociodemographic characteristics and prevalence of HIV, HBV, and HCV in people who inject drugs: a multistage systematic review. Lancet Glob Health, 5(12): e1192–e1207.
2 McCarron P and Smyth BP (2023) Changes in HIV incidence in people who inject drugs in Ireland from 2000 to 2018: longitudinal observational study. Addiction, 118(6): 1177–1181. Available from: https://www.drugsandalcohol.ie/38061/
J Health care, prevention, harm reduction and treatment > Harm reduction > Substance use harm reduction
T Demographic characteristics > Person who injects drugs (Intravenous / injecting)
VA Geographic area > Europe > Ireland
Repository Staff Only: item control page